ESP8266 as bridge
This mode uses the ESP8266 to provide WIFI for a microcontroller as WIFI-TO-SERIAL BRIDGE.
Setup
- On the ESP8266 side the esp-link firmware is used
- On the Arduino / Similar side the OpenDevice + el-client library is used.
To flash ESP follow this guide: https://github.com/jeelabs/esp-link/blob/master/FLASHING.md
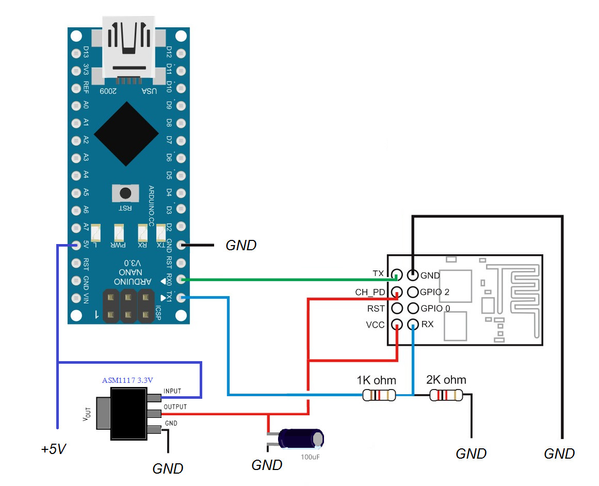
Hardware Connections
| Arduino | ESP8266 |
|---|---|
| RX (0) | TX |
| TX (1) | RX |
It is recommended to use an external power supply or converter to power the ESP8266
ESP-LINK Configuration
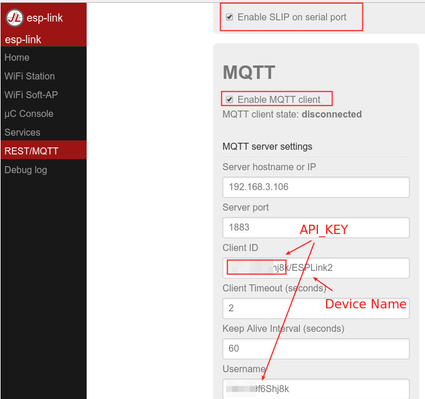
The communication between the ESP8266 and the server uses the MQTT protocol, for this we need:
- Enable SLIP on Serial port
- Enable MQTT
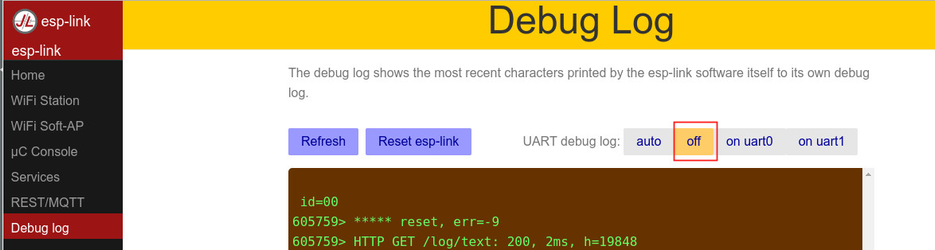
- Disable DEBUG log
- ClientID : ApiKey/ModuleName
- Username: ApiKey
- Password: x
Code
.....
Debug Information
You can enable debug information passing a second parameter.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> SoftwareSerial debugport(10,11); // RX, TX EspLinkConnection conn(Serial, debugport); // ... Serial.begin(115200); // ESP-Link port (change to correct port) debugport.begin(115200);
In Leonardo as it has two series, it does not need the SoftwareSerial
You can also see some debug information on the Esp-Link web console
References
- http://www.martyncurrey.com/arduino-to-esp8266-serial-commincation/
- https://github.com/jeelabs/el-client/tree/master/ELClient
- https://github.com/jeelabs/esp-link
, multiple selections available,